 Sep 8 2022
Sep 8 2022Media Release: Two Years into Old-Growth Strategic Review mandate, BC is failing to deliver change on the ground
For Immediate Release, September 8, 2022:
Two years into Old-Growth Strategic Review mandate, BC is failing to deliver change on the ground
Environmental organizations call for immediate action to make the promised paradigm shift a reality as at-risk forests continue to be destroyed
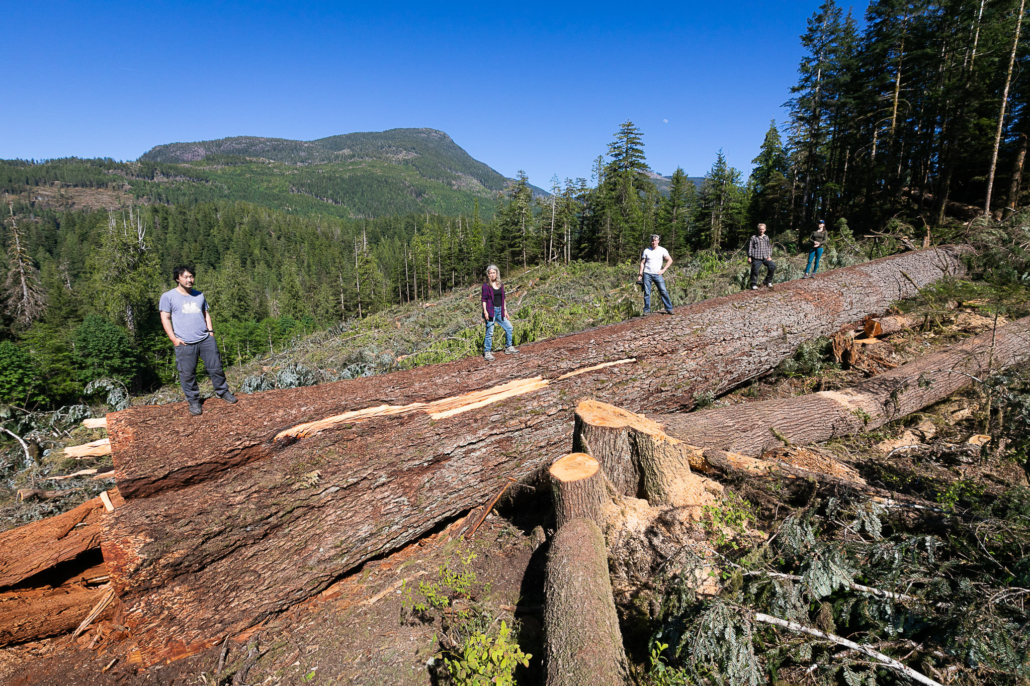
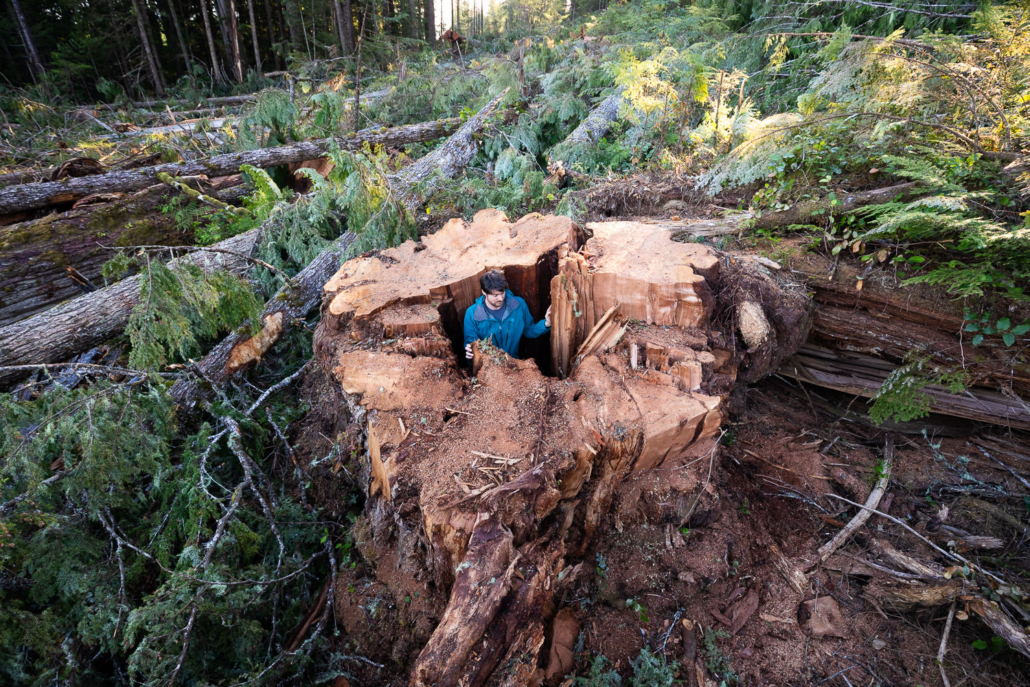
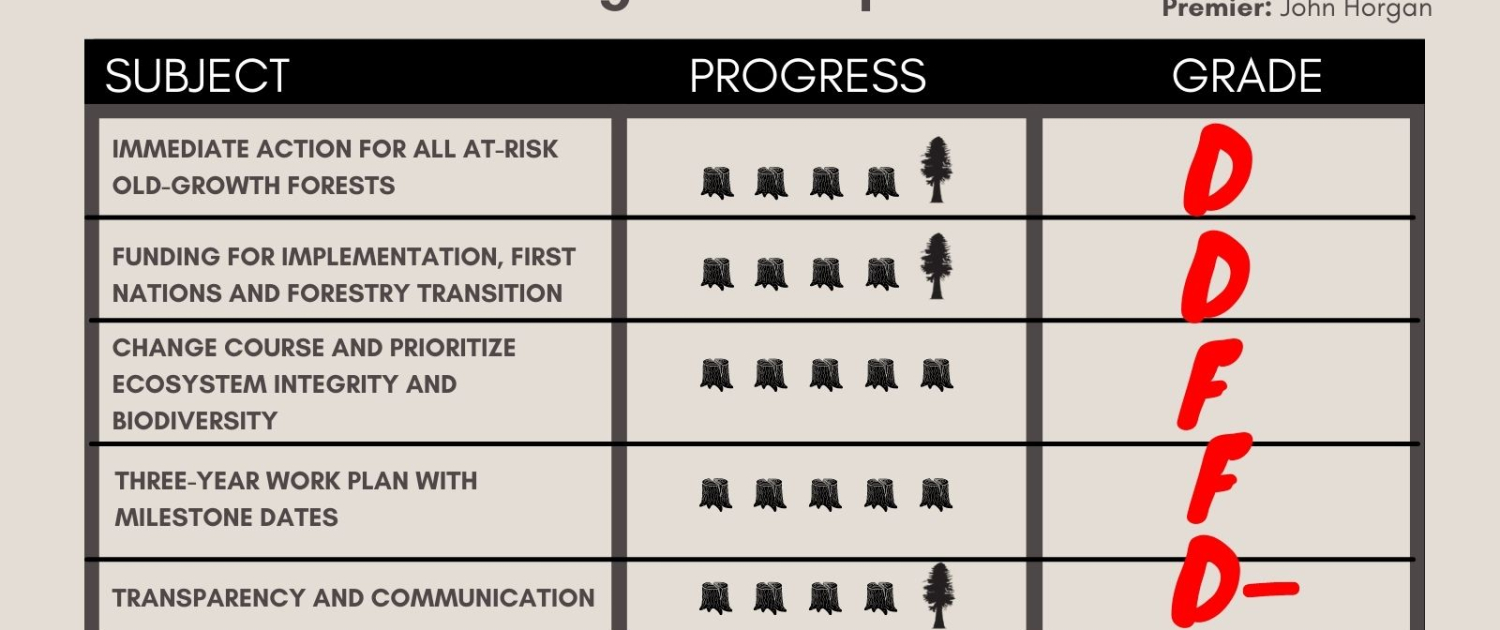
VICTORIA / UNCEDED LEKWUNGEN TERRITORIES – Two years after the provincial government released the report of its Old-Growth Strategic Review (OGSR) panel, Ancient Forest Alliance, Sierra Club BC, Stand.earth and the Wilderness Committee have given B.C. failing grades for its progress to protect threatened old-growth forests. Grades for four of five key issues fell since the last report card, with time running out to address delays before it’s too late to safeguard remaining endangered old-growth forests.
View Full Report Card Image Here
The OGSR report, released Sept. 11, 2020, makes clear recommendations to keep at-risk old-growth forests standing and overhaul forest stewardship within three years. However, the B.C. NDP government has fallen far behind, so far completing none of the panel’s 14 recommendations two-thirds of the way through the three-year timeline laid out in the report.
“Two of the three years to implement the B.C. government promises on old-growth have passed. Yet, clearcutting of irreplaceable, endangered old-growth continues, even in the most-at-risk stands,” says Jens Wieting, Senior Forest and Climate Campaigner at Sierra Club BC. “Instead of changing course, we are still marching towards ecosystem and climate breakdown. The window for action is closing. The next premier of B.C. must act swiftly before it’s too late.”
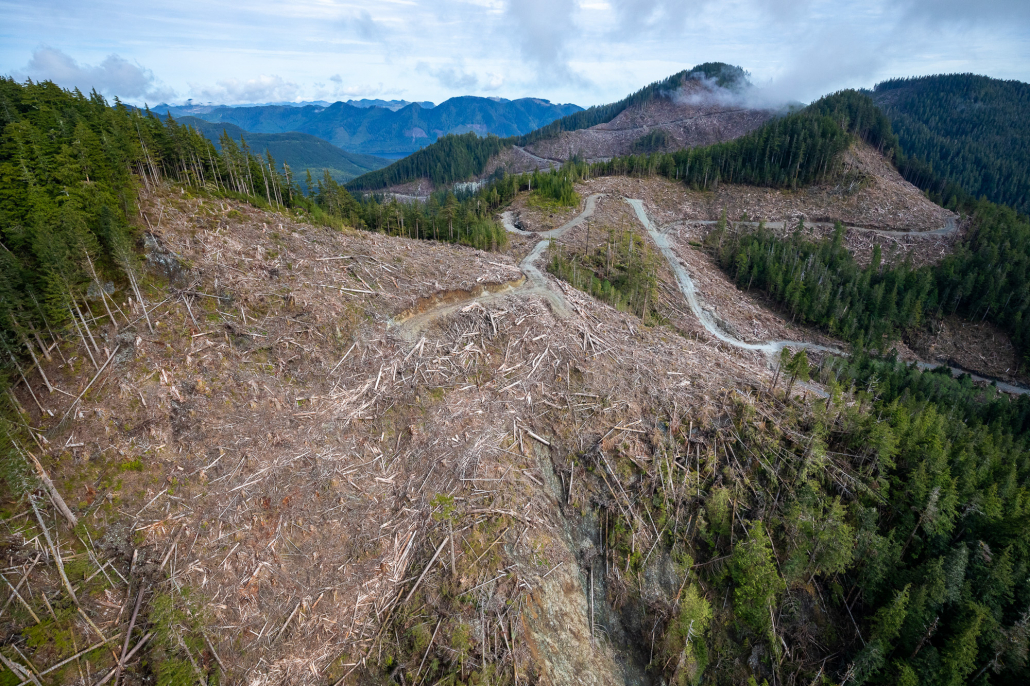

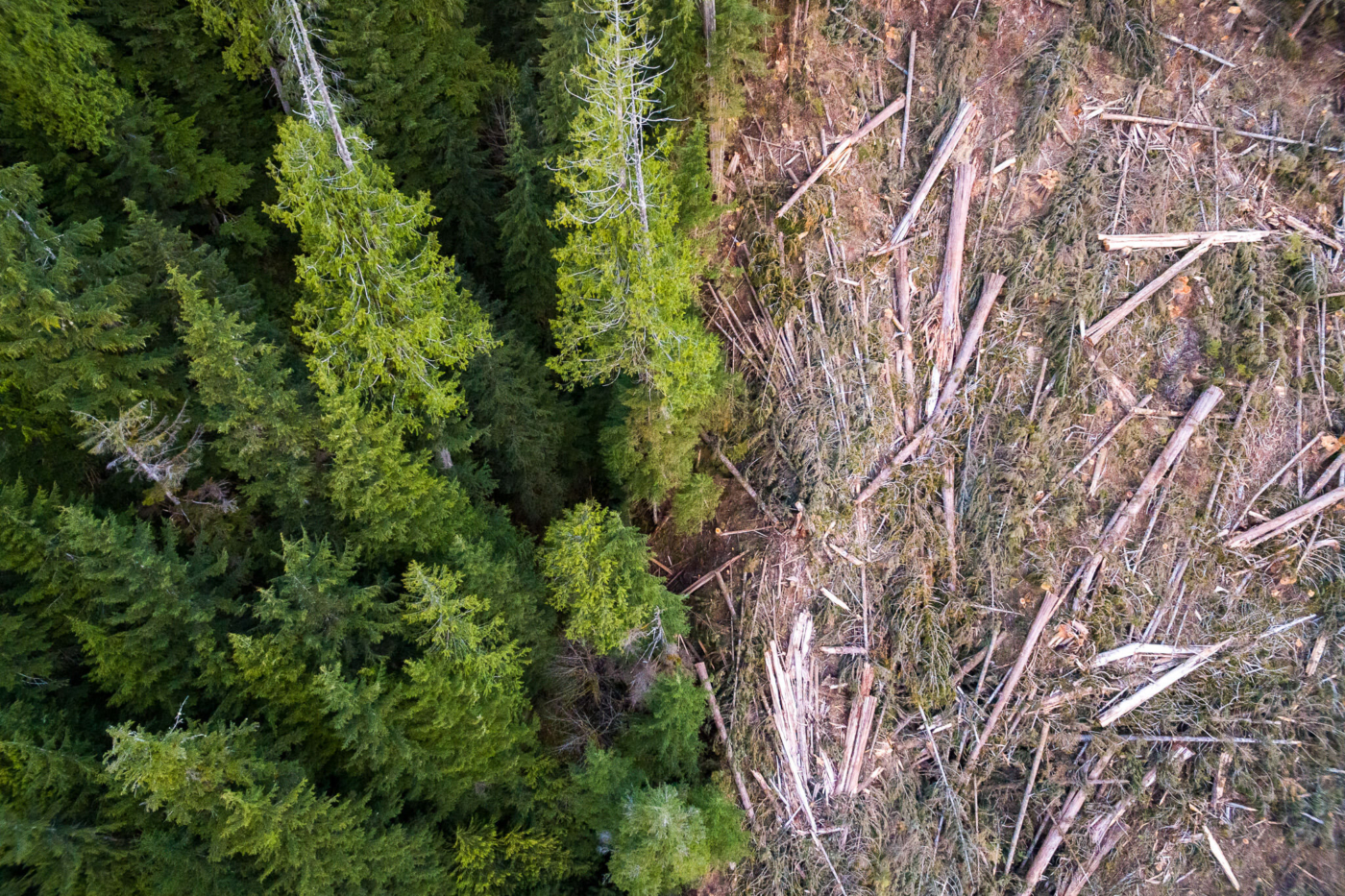
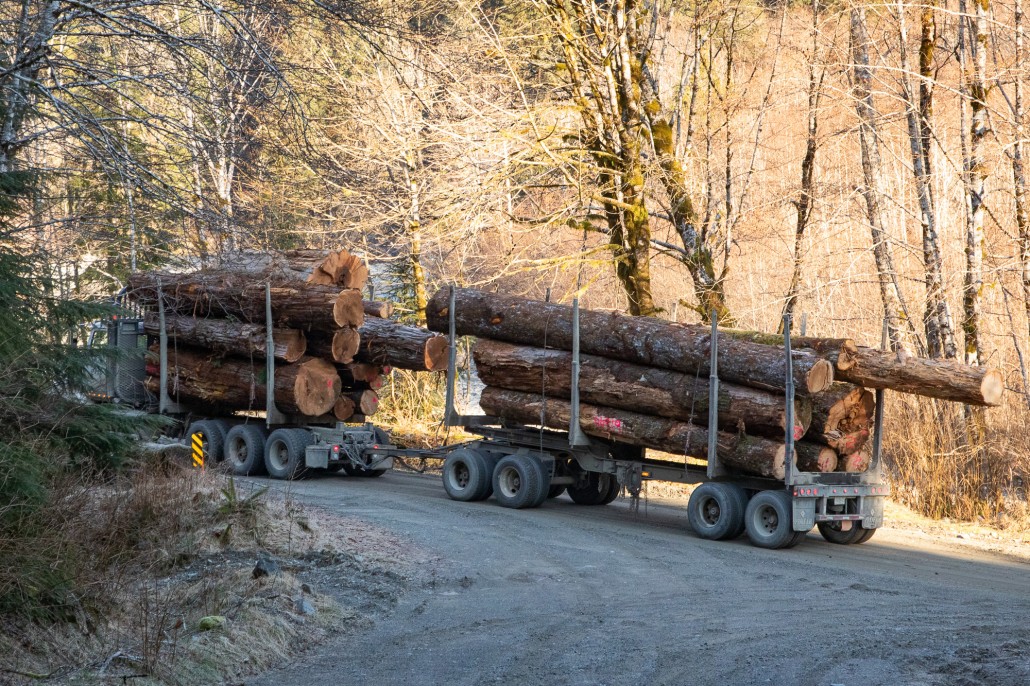
Following the assessment of a second expert group, the Technical Advisory Panel (TAP) in 2021, last November, the province released mapping of five million hectares of unprotected, at-risk old-growth and stated its intention to temporarily defer logging for about half of that (2.6 million hectares) considered most at-risk in the short-term. The TAP scientists emphasized deferrals were needed, especially for areas where logging was already planned, which they expected to encompass about 50,000 hectares. In April 2022, Forest Minister Katrine Conroy announced that a little over one million hectares of these deferrals had been finalized — leaving more than half of the most at-risk old-growth forests open for logging — but was unclear about which deferrals would actually stop permitted logging. Ongoing monitoring via field assessments and satellite analysis show clearcutting continues in stands recommended for deferral. It’s resulting in the loss of tens of thousands of hectares of the most ecologically valuable forests.
“With one hand, the province is signing off on logging and road building in proposed old growth deferrals, and with the other it’s congratulating itself for saving the forests,” says Tegan Hansen, Senior Forest Campaigner at Stand.earth. “Deferrals are meaningful when they stop logging, not as a political talking point. We need to see this government live up to its promises and prevent the destruction of the most at-risk old-growth forests.”
The B.C. NDP government has stated it will not halt logging without agreement from First Nations, but has not offered adequate funding to address the economic impacts of foregoing logging for short-term deferrals, or for long-term protection. The organizations are urging the province to immediately provide full financial support to First Nations to ensure logging is deferred in all at-risk old-growth forests, as called for by the Union of BC Indian Chiefs in June.
“If the province is serious about protecting old-growth, they must come forward with at least $300 million in conservation financing for First Nations to address the economic impacts of accepting short-term logging deferrals and enacting long-term protection measures for old-growth, and leverage the federal funding available to expand protected areas in Canada,” states TJ Watt of the Ancient Forest Alliance. “Without that funding, which the province must be fully aware is critical for these efforts to succeed, progress will remain stalled and irreplaceable ancient forests will continue to fall.”

In their bi-annual report card, the four organizations gave the B.C. government a D for funding provided to date, and the same grade for the deferrals enacted so far. For transparency and communication on old-growth, the province received a D-. And for changing course to prioritize ecological health and providing a three-year timeline to implement the OGSR’s recommendations, the province earned failing grades.
Over the summer, the provincial government has remained tight-lipped about old-growth forests. In the meantime, images of logging in proposed deferral areas have garnered attention and public frustration with the ongoing destruction of irreplaceable forests in B.C.
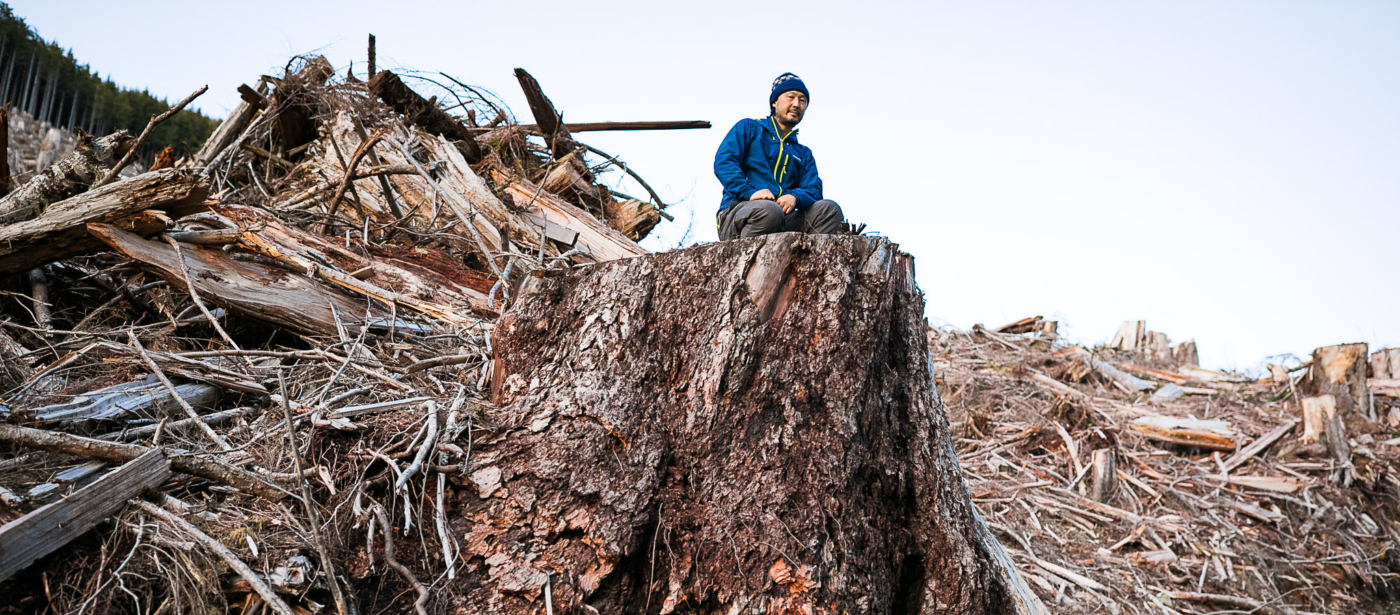
“The recommendations of the OGSR are clear and measurable, and this government told the public it would act on them with urgency. What we’ve seen in the two years since is the opposite, a slow, plodding approach that’s not at all indicative of a paradigm shift,” says Torrance Coste, National Campaign Director for the Wilderness Committee. “Ultimately, the score that matters is the one kept in the forests themselves. And the fields of fresh clearcuts in endangered old-growth underscore the NDP government’s failure to protect the most threatened forests.”
Ancient Forest Alliance, Sierra Club BC, Stand.earth, and the Wilderness Committee will continue to mobilize the public, document ongoing old-growth logging and partner with First Nations, community groups, municipalities, unions and businesses to advance meaningful protection for threatened old-growth forests and a paradigm shift that puts ecological integrity and the wellbeing of communities over short-term timber values.







